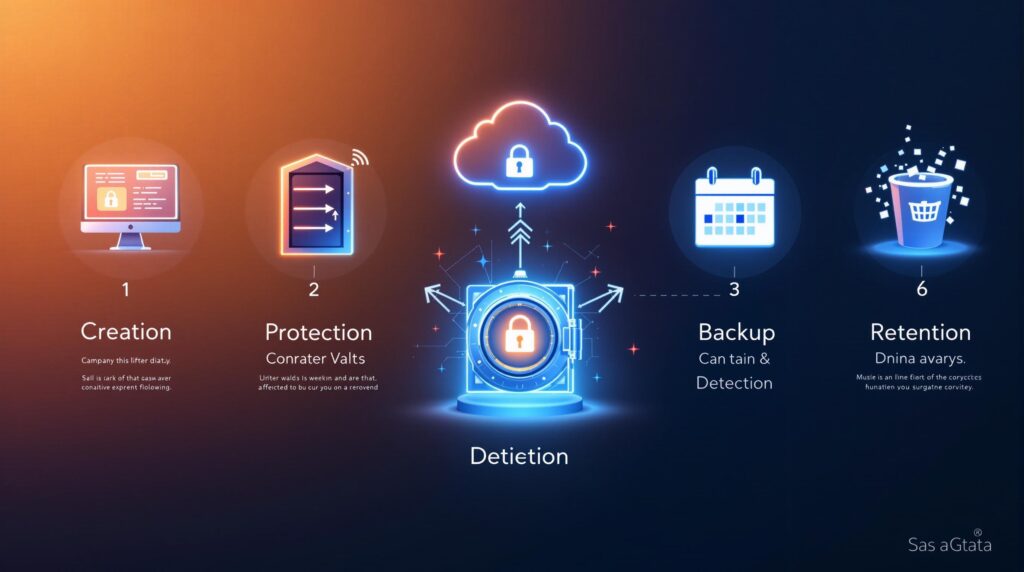
SaaS data management is critical as businesses increasingly rely on cloud services. Here’s a quick breakdown of the 5 key stages of the SaaS data lifecycle and why they matter:
- Creation: Data originates from user activities, automated workflows, integrations, and APIs. Risks include unencrypted files and improper permissions.
- Protection: Safeguard active data with role-based access, MFA, and real-time monitoring. Human errors cause 68% of SaaS data loss.
- Backup: Use strategies like the 3-2-1-1 rule for redundancy and quick recovery. Automated backups are essential for long-term security.
- Retention: Balance compliance (e.g., HIPAA, GDPR) with cost-effective storage. Tiered retention policies can reduce expenses.
- Deletion: Ensure secure removal of data using cryptographic erasure and automated workflows while maintaining compliance records.
Quick Stats:
- 60% of data loss stems from human error.
- 83% of enterprises rely on automated backup solutions.
- Ransomware attacks on Microsoft 365 rose 37% year-over-year.
This lifecycle approach helps businesses secure, retain, and delete data effectively while staying compliant and reducing risks.
What is Backup Lifecycle Management?
Stage 1: Data Creation
Managing data effectively starts right where it’s created. In SaaS environments, data creation has grown more complex than just uploading files. Today, 68% of SaaS data comes from automated systems rather than manual input . For instance, a single user in Microsoft 365 generates around 3.2GB of new data each month, largely through activity on Teams and SharePoint .
Key sources of data creation include:
- User Activities: Emails, documents, and files. For example, over 148 million Google Drive files are created daily .
- Automated Workflows: Scheduled reports and updates, such as 25 million Teams messages sent daily .
- Third-Party Integrations: Tools like CRM systems, with 45% of organizations using four or more apps to sync data .
- API-Driven Processes: Automated backups and data synchronization.
Data Creation Risks
The rapid growth of SaaS data – 33% annually – creates immediate challenges, especially for storage and backups . On average, files in Office 365 exist in 18 different versions across various locations, leading to inefficiencies and potential confusion .
“Data creation now includes collaborative edits and API transactions requiring immediate protection.” – Arcserve Unified Data Protection Whitepaper
Security risks during this stage are also a concern. Some of the most common vulnerabilities include:
- Unencrypted collaborative files, which can expose sensitive information .
- Improper permissions on shared documents, leading to unauthorized access .
- Malware threats from auto-synced attachments .
To address these challenges, organizations should prioritize strategies like real-time data verification and mandatory metadata labeling . These actions help ensure data is protected from the moment it’s created.
Stage 2: Data Protection During Use
Once data is created, the next challenge is keeping it safe during active use – when it’s most at risk. With 68% of SaaS data loss happening during day-to-day operations due to accidental deletions and overwrites , protecting data in use requires strong security measures. On average, organizations experience 12.7 synchronization errors per month across their SaaS platforms , underscoring the importance of having solid safeguards in place.
Ways to Protect Data in Use
Effective data protection relies on multiple layers of security working together. Here are some key methods:
- Role-based access controls: Limit access to reduce exposure risks by 68% .
- Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA): Add an extra layer of security for administrative actions.
- Version control systems: Keep at least 30 revisions to recover from accidental changes .
- Checksum validation: Identify 99.6% of partial upload issues .
Common Risks During Active Data Use
Data loss during use often stems from human mistakes and technical glitches. A 2024 SaaS incident report highlights the following leading causes:
| Risk Factor | Occurrence Rate |
|---|---|
| Misconfigured Automation | 32% of data loss incidents |
| Bulk Edit Errors | 28% of unintended changes |
| Permission Overrides | 19% of unauthorized access cases |
| API Rate Limit Breaches | 41% of integration failures |
Advanced AI tools now monitor over 120 types of user interactions to spot unusual behavior . This approach has cut breach response times by 83% compared to manual monitoring . Automated systems also create emergency restore points during mass deletions or unusual activity .
These real-time measures act as a safety net, complementing scheduled backups to ensure data remains secure.
Stage 3: Backup Implementation
After establishing real-time protection in Stage 2, the next step is setting up a reliable backup system to safeguard data over the long term. According to Arcserve’s 2024 data protection survey, 92% of enterprises now use a mix of automated and on-demand backups , ensuring their data is well-protected.
Choosing the Right Backup Method
Selecting the right backup approach depends on how critical the data is and any compliance requirements. For example, financial records or essential operational data may require frequent backups throughout the day, while less critical information might only need daily snapshots . A widely recommended approach is the 3-2-1-1 rule:
| Component | Requirement | Purpose |
|---|---|---|
| 3 Copies | Keep three total copies | Ensures redundancy |
| 2 Media Types | Use two different formats | Guards against media failure |
| 1 Offsite | Store one copy remotely | Protects against disasters |
| 1 Immutable | Keep one unchangeable copy | Defends against ransomware |
Backup schedules should align with an organization’s recovery time objectives (RTOs) and recovery point objectives (RPOs). These metrics help determine how often backups should occur, based on operational needs and acceptable risk levels .
Features of CloudAlly Backup
CloudAlly offers a robust backup solution with features designed for enterprise needs, including unlimited retention and precise restoration capabilities. Key features include:
| Feature | Implementation | Business Impact |
|---|---|---|
| Backup Frequency | Daily automated + on-demand | Provides flexible scheduling options |
| Recovery Granularity | Item-level restoration | Achieves <15-minute restore times for most cases |
| Search Capability | Metadata-based filtering | Speeds up incident response by 67% |
| Security Standards | AES-256 encryption + OAuth/MFA | Meets NIST 800-88 guidelines |
The platform’s metadata-aware search simplifies locating specific files without performing full system rollbacks, significantly reducing downtime .
Additionally, modern backup solutions prioritize cross-platform compatibility. This ensures smooth data transfers between services while preserving metadata integrity, which is crucial for maintaining business operations during migrations or unexpected disruptions. CloudAlly also guarantees 99.95% availability, offering peace of mind for enterprises .
sbb-itb-3f51f55
Stage 4: Data Retention and Storage
After setting up backups, organizations need to define retention policies that align with both business goals and legal requirements. Managing data retention in SaaS environments involves balancing compliance, cost, and accessibility.
Retention Rules and Laws
Retention periods vary by data type and regulatory requirements. For instance, financial records often need to be kept for over 7 years for tax compliance, while healthcare organizations must retain patient records for at least 6 years under HIPAA guidelines .
| Industry | Retention Period | Key Requirements |
|---|---|---|
| Healthcare (HIPAA) | 6 years minimum | Audit trails, encrypted storage |
| Financial Services | 7+ years | Immutable records, versioning |
| General Business (GDPR) | Purpose-limited | Documented justification |
Organizations can reduce costs while staying compliant by using tiered retention policies. This method automatically moves infrequently accessed data to cost-effective storage options while keeping frequently used data easily accessible.
Long-term Storage Options
Modern SaaS backup tools offer a range of storage solutions to meet diverse business needs. Built-in SaaS storage often comes with limited retention windows, while third-party options provide greater flexibility.
| Storage Type | Built-in SaaS | Third-Party |
|---|---|---|
| Retention Period | 30-180 days typical | Customizable |
| Geographic Control | Limited | Multiple region options |
| Cost Structure | Platform subscription | Usage-based pricing |
| Compliance Tools | Basic versioning | Advanced audit features |
For enterprises, platforms like CloudAlly provide encrypted, region-specific storage that complies with stringent regulations, including GDPR’s cross-border data transfer rules . Additionally, features like “Bring Your Own Storage” allow businesses to use their existing infrastructure while maintaining centralized management.
To manage long-term storage effectively, consider these strategies:
- Automate retention rules based on data type
- Monitor costs and retrieval metrics
- Conduct quarterly audits
- Use storage tiers for better cost management
These steps help ensure compliance and streamline the transition from retention to secure deletion.
Stage 5: Data Deletion
The final step in the data lifecycle is secure deletion. This process is essential to protect sensitive information and ensure compliance with legal and regulatory standards.
Secure Data Removal Methods
Effective data deletion requires addressing both active storage and backups to prevent any chance of recovery. Here’s a breakdown of common methods:
| Deletion Method | Purpose | Implementation |
|---|---|---|
| Cryptographic Erasure | Makes data unreadable | Delete encryption keys |
| Media Sanitization | Prevents forensic recovery | Overwrite with zeros and verify processes |
| Automated Deletion | Supports compliance | Schedule regular purges based on retention rules |
| Backup Cleanup | Stops data reintroduction | Remove data from all backups and archives |
These strategies often integrate into automated workflows, ensuring deletion is consistent across all systems. Platforms like CloudAlly use such workflows to enforce deletion policies across backups.
Deletion Records and Reports
After securely deleting data, organizations must document the process to demonstrate compliance and accountability. Proper documentation ensures transparency and provides proof for audits.
| Documentation Element | Required Information | Purpose |
|---|---|---|
| Audit Trails | User actions, timestamps, logs | Tracks deletion history and accountability |
| Deletion Certificates | Verification of complete removal | Confirms compliance for auditors |
| Activity Reports | Details on who, what, and when | Monitors deletion processes |
| Compliance Records | Proof of meeting regulations | Demonstrates legal adherence |
For example, Google Cloud uses a multi-stage pipeline to delete customer data within 180 days, ensuring thorough removal while maintaining detailed records .
To enhance deletion documentation:
- Assign clear oversight roles and automate logging systems.
- Keep approval records and verification processes up to date.
- Regularly generate compliance audit reports.
Organizations should also validate audit logs and update logging systems when introducing new workflows . This ensures every step, from initiation to completion, is thoroughly documented.
Summary: SaaS Data Management Best Practices
Effective SaaS data lifecycle management combines strong protection, efficient storage, and strict compliance. The National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST) defines the data lifecycle as including “creation or collection, processing, dissemination, use, storage, and disposition, including destruction or deletion” .
Data Protection and Storage
The 3-2-1-1 backup strategy is a reliable method to safeguard data. This involves keeping three copies of data, using two different media types, storing one copy offsite, and ensuring one copy is immutable. This setup ensures redundancy and supports quick recovery across all stages of the data lifecycle .
Access Control and Security
Implementing robust security measures such as Role-Based Access Control (RBAC) and Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA) is key to protecting data. Tools like CloudAlly provide granular control over Office 365 data, enhancing security at every stage.
Automation and Compliance
Data loss affects 80% of businesses . Automating processes like daily backups, compliance monitoring, and user lifecycle management reduces human error and maintains consistency throughout the data lifecycle.
Data Retention and Recovery
Balancing retention policies with practical needs is crucial. Microsoft notes that “If you want to support recovering messages beyond 30 days, you would need to use a 3rd party service for the backup… Point in time restoration of mailbox items is out of scope for the Exchange Online service” . This highlights the importance of external tools for extended data recovery.
Risk Management
Human error is a leading cause of data loss. To mitigate this, organizations should establish clear data handling policies, conduct regular training, automate safeguards, and maintain comprehensive audit trails.
Technology Integration
With mid-sized businesses managing an average of 1,250 SaaS applications , specialized tools are critical for managing the data lifecycle effectively. These tools ensure coordinated protection and reduce the risk of data loss.
These practices, reinforced by regulations like GDPR, help build a robust approach to data management.
“Have the ability to restore the availability and access to personal data in a timely manner in the event of a physical or technical incident.” – Article 32, GDPR
FAQs
What is the data lifecycle management policy?
A data lifecycle management (DLM) policy focuses on maintaining security, accuracy, and availability of data . Here’s what a DLM policy covers:
- Data Security: Protects against unauthorized access using encryption and access controls.
- Data Integrity: Ensures data remains accurate and free from errors.
- Data Accessibility: Makes it easy for authorized users to retrieve data when needed.
Research highlights that human error causes 43% of data loss incidents . To tackle this, centralizing data management through a customer data platform (CDP) can help streamline tracking and management .
These principles align with the structured stages of the data lifecycle explained below.
What are the 5 stages of data life cycle management?
The data lifecycle in SaaS environments consists of five key stages, each with specific activities and considerations:
| Stage | Key Activities | Key Considerations |
|---|---|---|
| Creation | Collecting data | Maintain consistent tracking and quality. |
| Processing & Storage | Organizing and securing data | Use encryption and backup systems. |
| Usage | Utilizing data | Monitor access and ensure proper usage. |
| Archiving | Preserving data | Follow retention rules and regulations. |
| Destruction | Removing data | Use proper sanitization methods. |
To implement these stages effectively, focus on collecting first-party data and staying compliant with regulations like GDPR and HIPAA .